Investing has become a popular way to grow wealth, but it can be confusing for beginners to understand the different approaches. Active and passive investing are two of the most common strategies, but what sets them apart?
Active investing involves actively managing a portfolio, making frequent trades to try and outperform the market. Passive investing, on the other hand, involves buying and holding a diversified portfolio that tracks a market index. Let’s dive deeper into the differences between these two approaches and how they can impact your investment returns.
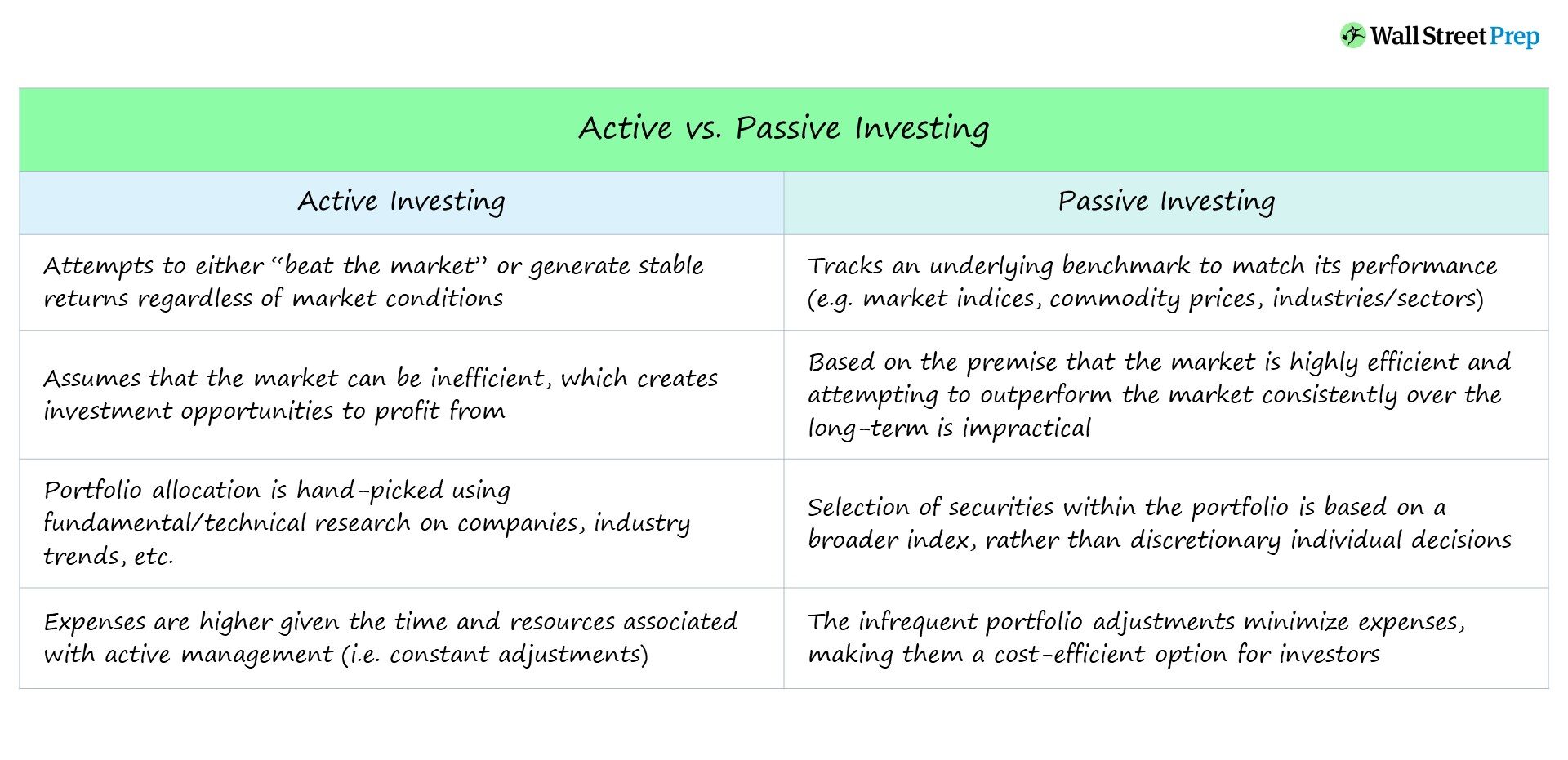
Active investing involves buying and selling securities with the goal of outperforming the market, while passive investing seeks to match the market’s returns by holding a diversified portfolio of securities. Active investors rely on research and analysis to make trading decisions, while passive investors typically invest in index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Active investing may provide higher returns but also carries higher risk and requires more time and effort, while passive investing is more hands-off and may offer lower fees and taxes.
Understanding the Difference Between Active and Passive Investing
Investing is the process of allocating resources, usually money, with the expectation of generating profit or income. When it comes to investing, there are two main approaches: active and passive. Both strategies have their benefits and drawbacks, and it’s important to understand the differences between them before deciding which one is right for you.
Active Investing
Active investing involves buying and selling securities with the goal of outperforming the market. This approach often involves a significant amount of research, analysis, and decision-making. Active investors believe they can identify mispricings in the market and generate higher returns by buying undervalued securities and selling overvalued ones.
One of the main advantages of active investing is the potential for higher returns. Skilled active investors can make strategic decisions and generate alpha, or returns that beat the market. Additionally, active investors have more control over their investments and can make adjustments to their portfolio based on changing market conditions.
However, active investing also comes with some drawbacks. It requires a significant amount of time, resources, and expertise to be successful. Active investors must stay up-to-date on market trends, economic indicators, and company news, which can be time-consuming. Additionally, active investing can be more expensive than passive investing due to higher transaction costs and management fees.
Passive Investing
Passive investing involves buying and holding a diversified portfolio of securities that mirrors a market index. This approach does not involve attempting to outperform the market but rather seeks to match the performance of the index. Passive investors believe that markets are efficient and that it is difficult, if not impossible, to consistently outperform the market.
One of the main advantages of passive investing is its simplicity. Passive investors do not need to conduct extensive research or make complicated investment decisions. Instead, they can invest in a low-cost index fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that tracks a market index. Passive investing is also generally less expensive than active investing, as it involves fewer transactions and lower management fees.
However, passive investing also has some drawbacks. Because it seeks to match the market, passive investing does not offer the potential for higher returns that active investing does. Additionally, passive investors have less control over their investments and must accept the performance of the market, even during periods of volatility or downturns.
Active vs. Passive Investing
When deciding between active and passive investing, there are several factors to consider. Here are some key differences between the two approaches:
Performance: Active investing offers the potential for higher returns, but it also involves more risk and requires more skill and expertise. Passive investing seeks to match the market and offers lower risk but also lower returns.
Cost: Active investing is generally more expensive than passive investing due to higher transaction costs and management fees. Passive investing is more cost-effective and involves fewer fees.
Control: Active investors have more control over their investments and can make adjustments based on changing market conditions. Passive investors have less control but also less responsibility for their investments.
Risk: Active investing involves more risk than passive investing, as it requires making strategic decisions and identifying mispricings in the market. Passive investing involves less risk but also less potential for high returns.
Expertise: Active investing requires significant expertise and knowledge of the market. Passive investing is more accessible to novice investors and requires less knowledge and expertise.
Tax Efficiency: Passive investing is generally more tax-efficient than active investing, as it involves fewer transactions and generates fewer taxable events.
Conclusion
In summary, active and passive investing are two distinct approaches to investing. Active investing involves attempting to outperform the market through strategic decisions and analysis, while passive investing involves matching the market through index funds or ETFs. Both approaches have their benefits and drawbacks, and it’s important to consider your investment goals, risk tolerance, and expertise before choosing between them. Ultimately, the best approach will depend on your individual circumstances and financial objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Active Investing?
Active investing is a strategy where an investor buys and sells securities in an attempt to outperform the market. The goal is to beat the average returns of a particular market index or benchmark. Active investors typically rely on research, market trends, and their own intuition to make investment decisions. They are often more hands-on and spend more time analyzing and managing their portfolios.
Active investing can be more expensive than passive investing because of the higher costs associated with trading and research. Active investors also take on more risk because their portfolios are less diversified and they are more exposed to market fluctuations.
What is Passive Investing?
Passive investing is a strategy where an investor buys a diverse portfolio of securities and holds onto them for the long-term. The goal is to match the returns of a particular market index or benchmark. Passive investors typically rely on low-cost index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) to achieve this goal. They are less hands-on and spend less time managing their portfolios.
Passive investing is generally less expensive than active investing because of the lower costs associated with trading and research. Passive investors also take on less risk because their portfolios are more diversified and they are less exposed to market fluctuations.
What are the advantages of Active Investing?
The main advantage of active investing is the potential for higher returns. Active investors have the ability to outperform the market and earn higher returns than passive investors. They can also invest in specific sectors or industries that they believe will perform well, which can lead to higher returns.
Active investing also allows investors to be more involved in the management of their portfolios. They can make decisions based on their own research and intuition, which can be empowering.
What are the advantages of Passive Investing?
The main advantage of passive investing is the lower cost. Passive investors typically pay lower fees than active investors because they are not paying for research or trading costs. This can lead to higher returns over the long-term.
Passive investing is also less risky than active investing because of the diversification of the portfolio. By investing in a broad range of securities, passive investors are less exposed to market fluctuations and individual stock risk.
Which is better: Active or Passive Investing?
There is no definitive answer to this question because the best type of investing strategy depends on your individual goals, risk tolerance, and investment style. Active investing may be a good choice for those who are willing to put in the time and effort to research and manage their portfolios. Passive investing may be a good choice for those who want a more hands-off approach and are focused on long-term returns.
Ultimately, the decision between active and passive investing should be based on your personal preferences and financial goals. It is also important to remember that both strategies have their advantages and disadvantages, and there is no one-size-fits-all approach to investing.
What is Active and Passive Investing?
In conclusion, understanding the difference between active and passive investing is crucial for any investor looking to make informed decisions with their money. Active investing involves a hands-on approach, with investors actively choosing and managing their portfolio. On the other hand, passive investing involves investing in a pre-determined portfolio, with little to no active management.
While both active and passive investing have their pros and cons, it ultimately comes down to the individual investor’s preferences and financial goals. Active investing may be more suitable for those who enjoy the thrill of the market and have the time and knowledge to actively manage their portfolio. Passive investing, on the other hand, may be more appropriate for those who prefer a more hands-off approach and are looking for a low-cost, diversified portfolio.
Regardless of which approach you choose, it’s important to do your research and make informed decisions based on your financial goals and risk tolerance. Ultimately, investing should be a long-term strategy that aligns with your overall financial plan, rather than a quick way to make a quick buck.