Margin accounts are a popular investment tool that allows traders to buy securities by borrowing money from a broker. In this type of account, traders can leverage their investments and potentially earn higher returns, but they also face higher risks.
Margin accounts work by providing traders with a line of credit, which they can use to purchase securities. However, traders must deposit a minimum amount of cash or securities into the account as collateral, and they must also pay interest on the borrowed funds. Understanding how margin accounts work is important for any investor looking to take advantage of this investment tool.
A margin account allows an investor to borrow funds from a broker to purchase securities. The investor is required to put down a percentage of the purchase price, called the margin, while the broker loans the remaining funds. This allows the investor to invest more money than they actually have on hand, potentially leading to greater profits. However, it also increases the risk of losses, as the investor may have to pay back the loan even if the investment loses value.
What is a Margin Account and How Does It Work?
Margin accounts have become increasingly popular among traders and investors in recent years. If you’re new to trading, you might be wondering what a margin account is and how it works. In simple terms, a margin account is a type of brokerage account that allows you to borrow money from your broker to invest in securities. This article will explore the basics of margin accounts and help you understand how they work.
What is a Margin Account?
A margin account is a type of brokerage account that allows you to borrow money from your broker to invest in securities. Essentially, it allows you to amplify your investment potential by leveraging your assets. With a margin account, you’re able to buy more securities than you would be able to with just the cash in your account.
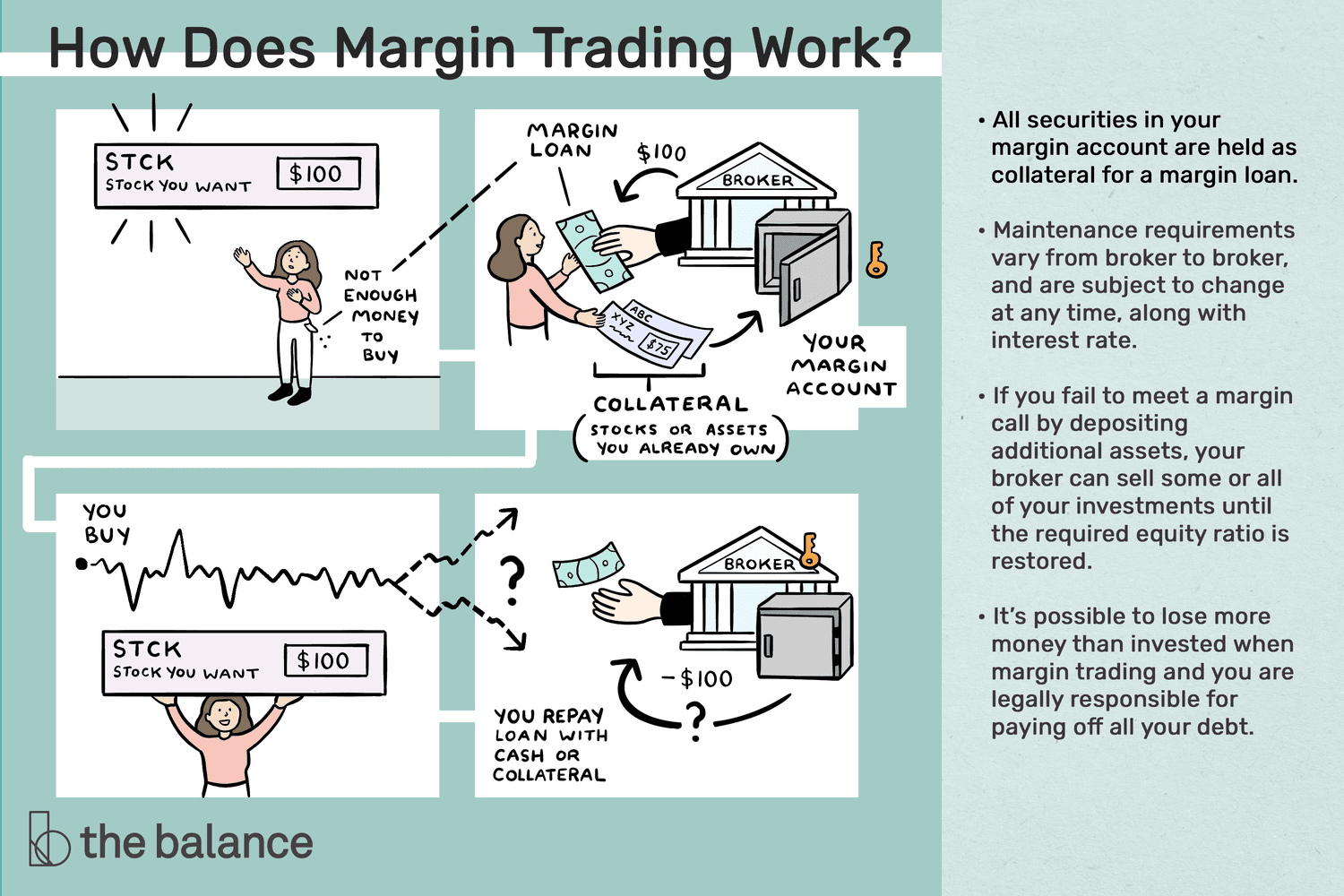
When you open a margin account, you’ll be required to deposit a certain amount of money as collateral. This collateral can be in the form of cash or securities. The amount of collateral required varies depending on the broker and the type of securities you want to invest in. Once you’ve deposited the required collateral, you’ll be able to borrow money from your broker to invest in securities.
How Does a Margin Account Work?
When you invest in securities using a margin account, you’re essentially borrowing money from your broker to buy more securities than you would be able to with just the cash in your account. The amount of money you’re able to borrow is determined by the amount of collateral you’ve deposited in your account.
For example, let’s say you have $10,000 in your margin account and you want to buy $20,000 worth of stock. Your broker might allow you to borrow the additional $10,000 to buy the stock, based on the collateral you’ve deposited in your account. In this scenario, you would have a margin level of 50%.
It’s important to remember that investing on margin comes with risks. If the value of your securities drops below a certain level, your broker may issue a margin call, which requires you to deposit more money into your account to maintain a certain level of collateral. If you’re unable to meet the margin call, your broker may sell your securities to cover the debt.
Benefits of a Margin Account
There are several benefits to opening a margin account. For one, it allows you to amplify your investment potential by leveraging your assets. With a margin account, you’re able to buy more securities than you would be able to with just the cash in your account.
Another benefit of a margin account is that it allows you to take advantage of opportunities that you might not be able to with just the cash in your account. If you see a stock that you believe is undervalued and likely to increase in value, a margin account can allow you to invest in it even if you don’t have the full cash amount available.
Margin Account vs. Cash Account
When deciding whether to open a margin account or a cash account, it’s important to understand the differences between the two. A cash account is a standard brokerage account in which you only trade securities using the cash available in your account.
In contrast, a margin account allows you to borrow money from your broker to invest in securities. This means that you’re able to buy more securities than you would be able to with just the cash in your account.
However, investing on margin also comes with risks. If your securities drop in value, you may be required to deposit more money into your account to maintain a certain level of collateral. If you’re unable to meet the margin call, your broker may sell your securities to cover the debt.
Margin Account Requirements
To open a margin account, you’ll need to meet certain requirements. These requirements will vary depending on the broker and the type of securities you want to invest in.
One requirement for opening a margin account is that you must have a certain amount of money in your account as collateral. This collateral can be in the form of cash or securities. The amount of collateral required will vary depending on the broker and the type of securities you want to invest in.
Another requirement for opening a margin account is that you must sign a margin agreement with your broker. This agreement outlines the terms and conditions of your margin account and the risks associated with investing on margin.
Margin Account Risks
Investing on margin comes with risks, and it’s important to understand these risks before opening a margin account. One risk is that if the value of your securities drops below a certain level, your broker may issue a margin call. This requires you to deposit more money into your account to maintain a certain level of collateral. If you’re unable to meet the margin call, your broker may sell your securities to cover the debt.
Another risk of investing on margin is that it can amplify your losses as well as your gains. If the securities you’ve invested in drop in value, you could lose more than the amount of money you’ve invested.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a margin account is a type of brokerage account that allows you to borrow money from your broker to invest in securities. It can be a useful tool for amplifying your investment potential and taking advantage of opportunities that you might not be able to with just the cash in your account.
However, investing on margin comes with risks, and it’s important to understand these risks before opening a margin account. If you’re considering opening a margin account, be sure to do your research and understand the requirements and risks involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a margin account?
A margin account is a type of brokerage account that allows investors to borrow money from the brokerage firm to purchase securities such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. This is also known as buying on margin. The investor is required to deposit a certain amount of money, known as the margin, in the account to act as collateral for the loan.
The margin allows the investor to leverage their investment and potentially earn higher returns. However, it also increases the risk of loss, as the investor is responsible for paying back the loan plus interest. If the value of the securities purchased with the loan drops below a certain level, the investor may be required to deposit additional funds or the brokerage firm may sell the securities to cover the loan.
How does a margin account work?
In a margin account, the investor is able to purchase securities by borrowing money from the brokerage firm. This allows the investor to increase their buying power and potentially earn higher returns. The investor is required to deposit a certain amount of money, known as the margin, in the account to act as collateral for the loan.
The amount of margin required varies depending on the securities being purchased and the brokerage firm’s requirements. The investor pays interest on the amount borrowed, and the brokerage firm may also charge fees for maintaining the account and providing the loan. If the value of the securities drops below a certain level, the investor may be required to deposit additional funds or the brokerage firm may sell the securities to cover the loan.
What are the risks of using a margin account?
Using a margin account increases the risk of loss for the investor. If the value of the securities purchased with the loan drops below a certain level, the investor may be required to deposit additional funds or the brokerage firm may sell the securities to cover the loan. This is known as a margin call.
The investor is also responsible for paying interest on the amount borrowed, which can increase the cost of the investment. If the investor is unable to meet the margin call or pay back the loan, the brokerage firm may take legal action to recover the funds. It is important for investors to carefully consider the risks and potential benefits of using a margin account before opening one.
Who is eligible for a margin account?
To open a margin account, an investor must meet certain eligibility requirements. These requirements may vary depending on the brokerage firm, but typically include a minimum age of 18 and a certain level of investment experience and financial resources.
The brokerage firm may also consider factors such as the investor’s creditworthiness and investment objectives. Investors should carefully review the eligibility requirements and consider their own financial situation and investment goals before opening a margin account.
What are some alternatives to using a margin account?
Investors who are uncomfortable with the risks of using a margin account may consider alternative investment strategies. These may include diversifying their portfolio with a mix of stocks, bonds, and other securities, or using options and other derivatives to hedge their investments.
Investors may also consider using a cash account, which does not allow borrowing to purchase securities. While this may limit the investor’s buying power, it also eliminates the risk of a margin call and reduces the overall risk of loss. It is important for investors to carefully consider their investment goals and risk tolerance before deciding which investment strategy is right for them.
Trading 101: What is a Margin Account?
In conclusion, a margin account is a type of brokerage account that allows investors to borrow money from the broker to buy securities. This type of account can be useful for experienced investors who are looking to increase their buying power and potentially earn higher returns. However, it is important to understand the risks involved with using a margin account, including the possibility of losing more money than initially invested.
To open a margin account, investors must meet certain requirements, including having a minimum account balance and signing a margin agreement. Once approved, investors can use the funds provided by the broker to make trades, but they must also abide by certain rules and regulations, such as maintaining a minimum equity level in the account.
Overall, a margin account can be a powerful tool for investors looking to take on more risk and potentially earn higher returns. However, it is important to carefully consider the risks involved and to only use a margin account if you have a solid understanding of how it works and the potential consequences of using one.