Investing is a crucial way to grow your wealth over time, but with so many different types of investment accounts available, it can be overwhelming to know where to start. From traditional savings accounts to more complex options like stocks and mutual funds, there are many different ways to invest your money. In this article, we’ll explore the various types of investment accounts available to help you make informed decisions about your financial future.
There are several types of investment accounts, including individual retirement accounts (IRAs), 401(k)s, brokerage accounts, and mutual funds. IRAs and 401(k)s are tax-advantaged accounts that help you save for retirement, while brokerage accounts and mutual funds offer more flexibility in terms of investment options. Each type of account has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the one that best fits your financial goals and needs.
Understanding the Different Types of Investment Accounts
Investing is an essential part of wealth building and financial planning. But with various investment options available, it can be challenging to determine which type of investment account is suitable for your financial goals. Here, we’ll discuss the different types of investment accounts to help you make an informed decision.
1. Traditional Individual Retirement Account (IRA)
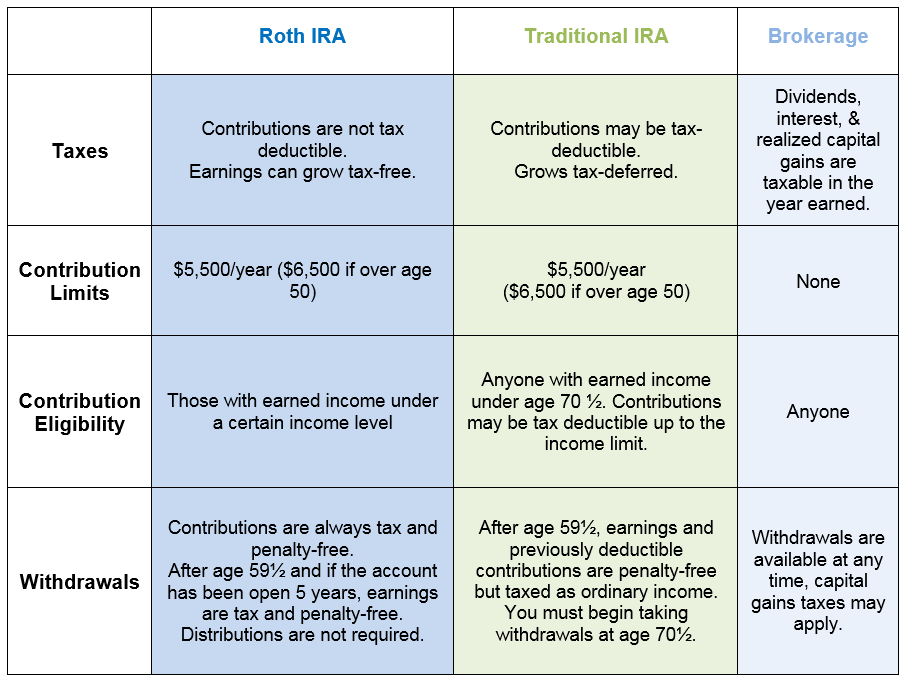
Traditional Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is a tax-deferred retirement account. Contributions made to a traditional IRA are tax-deductible, which means they reduce your taxable income. You’ll only pay taxes on the money you withdraw from your account.
The primary benefit of a traditional IRA is that it helps you save for retirement while reducing your taxable income. However, you’ll face penalties for early withdrawals before the age of 59½.
2. Roth IRA
A Roth IRA is an after-tax retirement account. Contributions made to a Roth IRA are not tax-deductible, but you won’t have to pay taxes on withdrawals made after the age of 59½.
The primary benefit of a Roth IRA is that it allows you to save for retirement and take advantage of tax-free growth. You can also withdraw contributions from your Roth IRA tax-free at any time.
3. 401(k) Plan
A 401(k) plan is an employer-sponsored retirement account. Contributions made to a 401(k) plan are tax-deferred, which means they reduce your taxable income. You’ll only pay taxes on the money you withdraw from your account.
The primary benefit of a 401(k) plan is that it allows you to save for retirement while reducing your taxable income. Additionally, some employers offer matching contributions, which can help boost your savings.
4. 403(b) Plan
A 403(b) plan is a retirement account for nonprofit employees, such as teachers or hospital workers. Contributions made to a 403(b) plan are tax-deferred, which means they reduce your taxable income. You’ll only pay taxes on the money you withdraw from your account.
The primary benefit of a 403(b) plan is that it allows you to save for retirement while reducing your taxable income. Additionally, some employers offer matching contributions, which can help boost your savings.
5. Taxable Brokerage Account
A taxable brokerage account is an investment account that allows you to buy and sell stocks, bonds, and other securities. You’ll pay taxes on any capital gains or dividends earned in your account.
The primary benefit of a taxable brokerage account is that it provides flexibility and liquidity. You can withdraw money at any time without penalty, and there are no contribution limits.
6. Health Savings Account (HSA)
A Health Savings Account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged account used to pay for qualified medical expenses. Contributions made to an HSA are tax-deductible, which means they reduce your taxable income. Withdrawals made for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.
The primary benefit of an HSA is that it allows you to save for medical expenses while reducing your taxable income. Additionally, unused funds roll over from year to year, and the account is portable if you change jobs.
7. Education Savings Account (ESA)
An Education Savings Account (ESA) is a tax-advantaged account used to save for qualified education expenses. Contributions made to an ESA are not tax-deductible, but withdrawals made for qualified education expenses are tax-free.
The primary benefit of an ESA is that it allows you to save for education expenses while taking advantage of tax-free growth. Additionally, you can use the funds for various education expenses, including tuition, books, and room and board.
8. Roth 401(k) Plan
A Roth 401(k) plan is an employer-sponsored retirement account that combines features of a 401(k) plan and a Roth IRA. Contributions made to a Roth 401(k) plan are after-tax, but withdrawals made after the age of 59½ are tax-free.
The primary benefit of a Roth 401(k) plan is that it allows you to save for retirement and take advantage of tax-free growth. Additionally, some employers offer matching contributions, which can help boost your savings.
9. Simple IRA
A Simple IRA is an employer-sponsored retirement account designed for small businesses with fewer than 100 employees. Contributions made to a Simple IRA are tax-deductible, which means they reduce your taxable income. You’ll only pay taxes on the money you withdraw from your account.
The primary benefit of a Simple IRA is that it allows small business owners to offer a retirement plan to their employees while reducing their taxable income. Additionally, some employers offer matching contributions, which can help boost employee savings.
10. SEP IRA
A SEP IRA is an employer-sponsored retirement account designed for self-employed individuals and small business owners. Contributions made to a SEP IRA are tax-deductible, which means they reduce your taxable income. You’ll only pay taxes on the money you withdraw from your account.
The primary benefit of a SEP IRA is that it allows self-employed individuals and small business owners to save for retirement while reducing their taxable income. Additionally, contributions can be made up until the tax-filing deadline, providing flexibility.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of investment accounts is essential to achieve your financial goals. Depending on your needs, you can choose an account that aligns with your financial objectives. Before making any investment decisions, it’s always best to consult with a financial advisor to ensure that your investment strategy suits your financial needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a brokerage account?
A brokerage account is a type of investment account that allows you to buy and sell securities, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. These accounts are offered by brokerage firms, which act as intermediaries between you and the financial markets. When you open a brokerage account, you deposit money into it and then use that money to make investments. You can choose to manage your own investments or work with a professional broker who can offer guidance and make investment decisions on your behalf.
While brokerage accounts offer a lot of flexibility and control over your investments, they also come with risks. The value of your investments can fluctuate based on market conditions, and there is no guarantee that you will earn a profit. It’s important to understand the risks and benefits of investing before opening a brokerage account.
What is a retirement account?
A retirement account is a type of investment account that is designed to help you save for retirement. These accounts offer tax benefits, which can help you maximize your savings over time. There are several different types of retirement accounts, including individual retirement accounts (IRAs), 401(k) plans, and pension plans.
One of the key benefits of retirement accounts is that they allow you to save for the future on a tax-deferred basis. This means that you don’t have to pay taxes on the money you contribute to the account until you withdraw it in retirement. Additionally, some retirement accounts offer employer matching contributions, which can help you build your savings faster.
What is a savings account?
A savings account is a type of investment account that is designed to help you save money for short-term goals, such as a vacation or emergency fund. These accounts typically offer lower interest rates than other types of investment accounts, but they also come with lower risk.
When you open a savings account, you deposit money into it and earn interest on that money over time. The interest rate on a savings account can vary depending on the bank or credit union that offers the account. While savings accounts are a safe option for short-term savings, they may not be the best choice for long-term investing.
What is a money market account?
A money market account is a type of investment account that is similar to a savings account. These accounts typically offer higher interest rates than savings accounts, but they also require a higher minimum balance. Money market accounts are often offered by banks and credit unions, and they are designed to be a low-risk way to earn interest on your savings.
One of the key benefits of a money market account is that your money is insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) up to $250,000. This means that even if your bank or credit union were to fail, your money would be protected. However, it’s important to remember that money market accounts are not risk-free, and the interest rate on these accounts can fluctuate over time.
What is a certificate of deposit (CD)?
A certificate of deposit (CD) is a type of investment account that allows you to earn a fixed interest rate over a set period of time. When you open a CD, you agree to leave your money in the account for a specific period of time, which can range from a few months to several years.
One of the key benefits of a CD is that it offers a guaranteed return on your investment. However, CDs also come with restrictions, such as early withdrawal penalties if you need to access your money before the end of the term. Additionally, the interest rate on a CD is typically lower than other types of investment accounts, such as stocks or mutual funds.
The 4 Best Types Of Investment Accounts
In conclusion, understanding the different types of investment accounts is essential for anyone who wants to invest their money wisely. From individual retirement accounts to taxable investment accounts, each type of account has its own unique set of benefits and drawbacks. By taking the time to research and compare the various options available, investors can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Ultimately, the key to successful investing is to stay informed and remain patient. While it can be tempting to chase quick gains or follow the latest investment trends, a well-rounded investment strategy requires a long-term focus and a commitment to diversification. By combining a variety of investment accounts and staying disciplined in your approach, you can build a strong financial foundation that will serve you well for years to come.
In the end, it’s important to remember that investing is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Everyone’s financial situation is unique, and the best investment strategy will depend on a variety of factors. By working with a trusted financial advisor and staying informed about the different types of investment accounts available, you can create a customized investment plan that meets your specific needs and helps you achieve your financial goals.