With the recent emergence of digital banking and a variety of new financial products, it can be difficult to decide which type of banking institution is best for you: a retail bank or a credit union. Both retail banks and credit unions offer a range of services, from checking and savings accounts to loans and investments, but the differences between them go beyond just the financial products they offer. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the pros and cons of retail banks and credit unions, so you can decide which type of institution is best for your needs.
| Retail Banks | Credit Unions |
|---|---|
| Provide a wider range of services, including investment and insurance products | Focus solely on banking services |
| Offer primarily conventional banking services | Offer mostly digital banking services |
| Offer fewer rewards and incentives | Offer more rewards and incentives |
| May have higher fees and interest rates | May have lower fees and interest rates |
| Have higher minimum balance requirements | Have lower minimum balance requirements |
Google Feature Snippet Answer:
Retail banks provide a wider range of services, including investment and insurance products, while credit unions focus solely on banking services. Retail banks offer primarily conventional banking services, while credit unions offer mostly digital banking services. Retail banks may have higher fees and interest rates, while credit unions may have lower fees and interest rates. Retail banks have higher minimum balance requirements, while credit unions have lower minimum balance requirements.
Retail Banks Vs Credit Unions: Comparison Chart
| Retail Banks | Credit Unions |
|---|---|
| Banks are usually profit-based institutions. | Credit unions are not-for-profit institutions, and they are typically owned by their members. |
| Banks often have a wide range of services, including traditional banking, investment accounts, credit cards, and other financial products. | Credit unions usually have fewer services and are typically limited to basic banking and loan services. |
| Banks often have branches in multiple locations and provide online banking services. | Credit unions may have fewer branches and may only offer limited online services. |
| Banks often have higher account minimums and higher fees. | Credit unions often have lower account minimums and lower fees. |
| Banks typically offer more credit products, such as credit cards, home loans, and other loan products. | Credit unions often offer fewer credit products and may have more stringent credit requirements. |
| Banks usually have more sophisticated technology and services. | Credit unions may have more limited technology and services. |
| Interest rates on savings accounts and other deposits are typically lower at banks. | Interest rates on savings accounts and other deposits are typically higher at credit unions. |
Contents
- Retail Banks vs Credit Unions
- Retail Banks Vs Credit Unions Pros & Cons
- Retail Banks Vs Credit Unions: Final Decision
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between a retail bank and a credit union?
- Do retail banks and credit unions offer the same services?
- Are retail banks more expensive than credit unions?
- Do retail banks and credit unions have different eligibility requirements for opening an account?
- Can I use my credit union debit card at a retail bank ATM?
- Banks vs. Credit Unions: What’s the Difference? | NerdWallet
Retail Banks vs Credit Unions
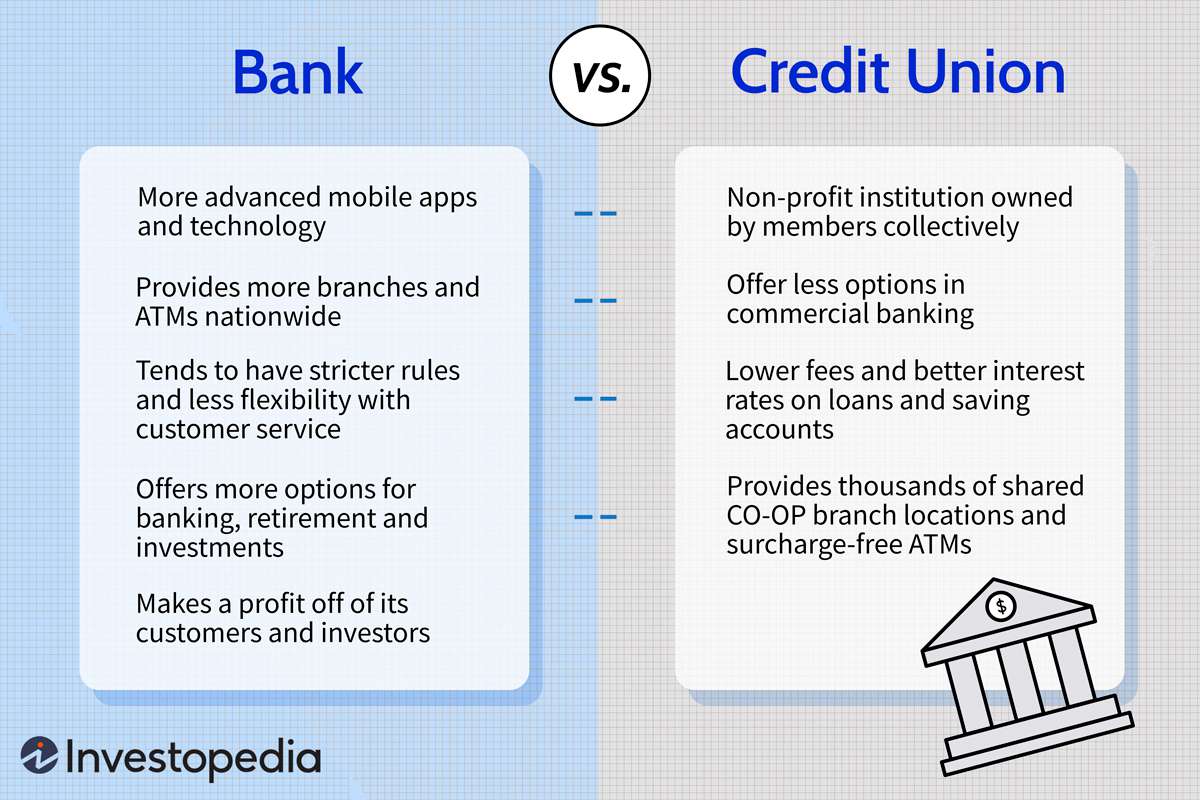
Retail banks and credit unions both offer financial services, but they have some distinct differences. Retail banks are for-profit businesses, while credit unions are non-profit organizations that are owned by their members. Retail banks have more branches and services, while credit unions have fewer branches and services.
Retail Bank Services
Retail banks offer a variety of services, including checking and savings accounts, loans, credit cards, and online banking. They also offer investment services, such as mutual funds and brokerage accounts. Retail banks also offer financial advice and assistance with retirement planning. Retail banks typically have more branches and ATMs than credit unions.
Retail banks are for-profit businesses, which means that they are focused on making a profit. This means that they may charge higher fees for their services, such as overdraft fees or monthly maintenance fees. Retail banks may also offer incentives and rewards programs that are designed to encourage customers to use their services.
Retail banks are typically large institutions that are owned by large banking corporations. They may be national or international, and they often have multiple branches in multiple cities. Retail banks may also have subsidiaries, such as mortgage companies, or other services such as insurance.
Credit Union Services
Credit unions are non-profit financial institutions that are owned by their members. Credit unions offer many of the same services as retail banks, including checking and savings accounts, loans, and credit cards. However, they typically have fewer branches and ATMs than retail banks.
Credit unions are owned by their members, which means that they are focused on providing the best service and rates to their members. Credit unions typically have lower fees and higher interest rates than retail banks. Credit unions also offer incentive programs and rewards programs to their members.
Credit unions are typically smaller institutions that are owned by their members. They are often local, and have only a few branches in their community. Credit unions may also offer other services such as insurance.
Retail Bank Advantages
Retail banks have more branches and ATMs than credit unions, which makes them more convenient for customers who need access to their funds. Retail banks also typically offer more services than credit unions, such as investment and retirement planning services. Retail banks may also offer incentive and rewards programs that can be beneficial to customers.
Retail banks may also offer lower fees than credit unions, as they are focused on making a profit. Retail banks are typically larger institutions that are owned by large banking corporations, which means that they may have more resources and access to capital than credit unions.
Retail banks are for-profit businesses, which means that they are focused on making a profit. This means that they may be more aggressive in competing for customers, which can be beneficial to customers who are looking for the best deals.
Credit Union Advantages
Credit unions are non-profit institutions that are owned by their members, which means that they are focused on providing the best service and rates to their members. Credit unions typically have lower fees and higher interest rates than retail banks. Credit unions also offer incentive programs and rewards programs to their members.
Credit unions are typically smaller institutions that are owned by their members, which means that they may have more flexibility in offering services and rates. Credit unions may also be more involved in the local community and may offer services that are tailored to the local area.
Credit unions are typically not-for-profit institutions, which means that they are focused on providing the best service and rates to their members. This means that they may be more willing to work with members who are having difficulty with their finances, or who are in need of financial assistance.
Retail Banks Vs Credit Unions Pros & Cons
- Retail Banks Pros
- Wide range of products and services
- Locations convenient to customers
- Modern technology and customer experience
- Highly regulated and secure
- Retail Banks Cons
- Higher fees for services
- Lower interest rates for deposits
- Less customer service
- Credit Unions Pros
- Lower fees for services
- Higher interest rates for deposits
- Better customer service
- Credit Unions Cons
- Limited products and services
- Fewer locations
- Less modern technology and customer experience
- Less regulated and secure
Retail Banks Vs Credit Unions: Final Decision
After weighing the pros and cons of retail banks and credit unions, the decision for which is better depends on the individual needs of the consumer. Both have advantages and disadvantages and it is up to the consumer to determine which is the best fit for their particular financial situation.
Retail banks offer a variety of services, convenience and access to international banking. They are often able to provide services that credit unions do not, such as international banking and currency exchange. They are generally larger and have more resources to offer customers. They can also usually provide a higher level of customer service.
Credit unions, on the other hand, are often smaller and more localized. They usually offer lower fees and interest rates on loans and savings accounts. They also offer more personalized services, as they are smaller and more focused on their members. They also often offer additional services, such as home and auto loans.
Ultimately, the decision of which is better – retail banks vs credit unions – is up to the consumer. Below are three reasons why one might choose the other:
- For those who need access to international banking services, retail banks are likely a better choice.
- For those who need more personalized service and lower fees and interest rates, credit unions may be the better option.
- For those who need both convenience and access to international banking services, as well as lower fees and interest rates, both may be a viable option.
Frequently Asked Questions
Retail banks and credit unions are two different types of financial institutions that provide banking services to individuals and businesses. Both offer deposit accounts, loans, and other financial services, but there are some differences in terms of fees, interest rates, and services offered.
What is the difference between a retail bank and a credit union?
A retail bank is a financial institution that provides banking services such as deposit accounts, loans, and other services to both individuals and businesses. Retail banks are typically owned by larger corporations, and profits generated by the bank are used to grow the corporation.
Credit unions, on the other hand, are not-for-profit organizations that are owned and operated by their members. Credit unions may provide similar services to retail banks, such as deposit accounts and loans, but they are structured differently. Credit unions are typically smaller and focus on providing more personalized services to their members.
Do retail banks and credit unions offer the same services?
Retail banks and credit unions offer many of the same services, such as deposit accounts, loans, and other services. However, retail banks typically offer more products and services than credit unions. Retail banks may also offer more advanced services such as online and mobile banking, investment products, and credit cards. Credit unions may also offer these services, but they may not be as comprehensive.
Are retail banks more expensive than credit unions?
Generally speaking, retail banks are more expensive than credit unions. Retail banks typically charge higher fees for their services and may have higher interest rates on loans. Credit unions, on the other hand, are typically more cost-effective, as they are not-for-profit organizations and typically pass their savings on to members in the form of lower fees and interest rates.
Do retail banks and credit unions have different eligibility requirements for opening an account?
Yes, retail banks and credit unions have different eligibility requirements for opening an account. Retail banks may have fewer requirements, as they are typically open to anyone who meets their minimum requirements. Credit unions, on the other hand, typically require that you be a member of the organization in order to open an account. To become a member of a credit union, you may need to meet certain requirements, such as living in a certain area or working for a specific company.
Can I use my credit union debit card at a retail bank ATM?
Yes, you can typically use your credit union debit card at a retail bank ATM. However, you may be charged a fee by the retail bank for using their ATM. Additionally, some credit unions may not be part of the same ATM networks as retail banks, so you may not be able to use your card at certain retail bank ATMs.
Banks vs. Credit Unions: What’s the Difference? | NerdWallet
In conclusion, retail banks and credit unions offer both advantages and disadvantages for customers, depending on their individual needs. Retail banks provide a wide range of banking services and products, often with higher fees, while credit unions provide fewer services, often with lower fees. Both banking institutions are beneficial to customers, but customers should carefully evaluate their financial needs before determining which institution is best for them.