Bonds have long been a popular investment vehicle for those seeking a steady income stream and a reliable return on investment. However, as with any investment, there are risks involved that investors should be aware of before jumping in.
From credit risk to interest rate risk, this article will explore the potential pitfalls of investing in bonds and provide tips for mitigating these risks to help you make better investment decisions. So, whether you’re a seasoned bond investor or just starting out, read on to learn more about the risks associated with investing in bonds.
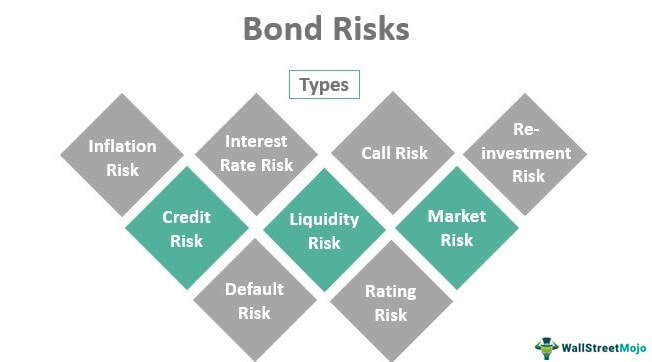
Investing in bonds comes with several risks, including interest rate risk, credit risk, inflation risk, and reinvestment risk. Interest rate risk refers to the possibility of losing money if interest rates rise, while credit risk involves the issuer defaulting on payments. Inflation risk occurs when the bond’s interest rate fails to keep up with inflation, and reinvestment risk arises when the bondholder reinvests proceeds at a lower rate. It’s essential to understand the risks before investing in bonds.
Contents
- What Are the Risks Associated With Investing in Bonds?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What factors can affect bond prices?
- What are the risks associated with corporate bonds?
- What are the risks associated with municipal bonds?
- What are the risks associated with government bonds?
- What are the risks associated with high-yield bonds?
- What Are The Risks Of Bonds? The Risks Of Investing In Bonds.
What Are the Risks Associated With Investing in Bonds?
Investing in bonds can be a great way to generate passive income over time. However, it’s important to understand the risks associated with this type of investment. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the different types of risks that come with investing in bonds and how you can mitigate them.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk is one of the biggest risks associated with investing in bonds. This risk arises from the fact that bond prices are inversely related to interest rates. As interest rates rise, bond prices fall, and vice versa. This means that if you invest in a bond with a fixed interest rate and interest rates rise, the value of your investment will decrease.
To mitigate interest rate risk, you can invest in bonds with variable interest rates or invest in a bond fund that holds a diversified portfolio of bonds with varying maturities.
Default Risk
Default risk is the risk that the issuer of the bond will be unable to make interest or principal payments to the bondholder. This risk is higher for bonds issued by companies with poor credit ratings or for bonds issued by countries with unstable political and economic conditions.
To mitigate default risk, you can invest in bonds issued by companies or countries with strong credit ratings or invest in a bond fund that holds a diversified portfolio of bonds.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that you won’t be able to sell your bond quickly enough if you need to cash out your investment. This risk is higher for bonds that are less actively traded or for bonds with longer maturities.
To mitigate liquidity risk, you can invest in bonds that are more actively traded or invest in a bond fund that provides daily liquidity.
Inflation Risk
Inflation risk is the risk that inflation will erode the purchasing power of your bond’s interest and principal payments over time. This risk is higher for bonds with fixed interest rates.
To mitigate inflation risk, you can invest in bonds with variable interest rates or invest in inflation-protected securities.
Call Risk
Call risk is the risk that the issuer of the bond will call the bond before its maturity date. This means that you’ll receive your principal back earlier than expected, which may result in reinvestment risk.
To mitigate call risk, you can invest in bonds with longer maturities or invest in callable bonds with a higher yield.
Currency Risk
Currency risk is the risk that the value of your bond’s interest and principal payments will be affected by changes in currency exchange rates. This risk is higher for bonds issued by foreign companies or countries.
To mitigate currency risk, you can invest in bonds issued in your home currency or invest in a bond fund that hedges against currency risk.
Reinvestment Risk
Reinvestment risk is the risk that you won’t be able to reinvest your bond’s interest payments at the same rate of return as your original investment. This risk is higher for bonds with longer maturities.
To mitigate reinvestment risk, you can invest in bonds with shorter maturities or invest in a bond fund that provides a steady stream of income.
Market Risk
Market risk is the risk that the overall bond market will decline, resulting in a decrease in the value of your bond investment. This risk is higher during times of economic downturns or recessions.
To mitigate market risk, you can invest in bond funds that hold a diversified portfolio of bonds or invest in bonds with higher credit ratings.
Tax Risk
Tax risk is the risk that changes in tax laws will affect the value of your bond investment. This risk is higher for bonds that are subject to higher tax rates.
To mitigate tax risk, you can invest in tax-exempt bonds or invest in a tax-efficient bond fund.
Summary
Investing in bonds can be a great way to generate passive income over time, but it’s important to understand the risks associated with this type of investment. By diversifying your portfolio, investing in bond funds, and understanding the different types of risks, you can mitigate the potential downside of investing in bonds and enjoy the benefits of this passive income stream.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors can affect bond prices?
Bonds are subject to price fluctuations, and several factors can impact their prices. One of the most significant factors is interest rates. When interest rates rise, bond prices tend to fall, and vice versa. Additionally, the creditworthiness of the issuer can impact bond prices. If an issuer’s credit rating is downgraded, its bonds may become less attractive to investors, leading to a drop in prices. Economic conditions, inflation rates, and geopolitical events can also impact bond prices.
In addition to these factors, there are also risks associated with specific types of bonds. For example, high-yield or junk bonds carry a higher risk of default than investment-grade bonds. Investors should carefully consider all of these factors before investing in bonds.
What are the risks associated with corporate bonds?
Corporate bonds are issued by companies to raise capital, and they can be an attractive investment option for many investors. However, they also carry certain risks. One of the primary risks associated with corporate bonds is credit risk. If the issuer of the bond experiences financial difficulties, it may be unable to make interest payments or repay the principal when the bond matures.
Another risk associated with corporate bonds is interest rate risk. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds decreases, which can lead to a decline in the price of the bond. Investors should carefully assess these risks before investing in corporate bonds.
What are the risks associated with municipal bonds?
Municipal bonds are issued by state and local governments to finance public projects. These bonds are generally considered to be less risky than corporate bonds, but they still carry certain risks. One of the primary risks associated with municipal bonds is credit risk. If the issuer of the bond experiences financial difficulties, it may be unable to make interest payments or repay the principal when the bond matures.
Another risk associated with municipal bonds is interest rate risk. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds decreases, which can lead to a decline in the price of the bond. Investors should carefully assess these risks before investing in municipal bonds.
What are the risks associated with government bonds?
Government bonds, also known as Treasury bonds, are issued by the federal government to finance its operations. These bonds are generally considered to be the safest type of bond, but they still carry certain risks. One of the primary risks associated with government bonds is interest rate risk. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds decreases, which can lead to a decline in the price of the bond.
Another risk associated with government bonds is inflation risk. If inflation rates rise, the purchasing power of the interest payments and principal may be eroded. Investors should carefully assess these risks before investing in government bonds.
What are the risks associated with high-yield bonds?
High-yield bonds, also known as junk bonds, are issued by companies with lower credit ratings. These bonds offer higher yields to compensate investors for the higher risk of default. One of the primary risks associated with high-yield bonds is credit risk. If the issuer of the bond experiences financial difficulties, it may be unable to make interest payments or repay the principal when the bond matures.
Another risk associated with high-yield bonds is liquidity risk. These bonds are less liquid than investment-grade bonds, which means they may be difficult to sell if the investor needs to raise cash quickly. Investors should carefully assess these risks before investing in high-yield bonds.
What Are The Risks Of Bonds? The Risks Of Investing In Bonds.
In conclusion, investing in bonds can be a smart way to diversify your portfolio and earn a steady stream of income. However, it is important to be aware of the risks associated with bond investing. These risks include interest rate risk, credit risk, and inflation risk.
To minimize these risks, it is important to do your research and carefully consider the creditworthiness of the issuer, the maturity of the bond, and the prevailing market conditions. Additionally, it may be wise to consult with a financial advisor who can help you make informed investment decisions.
Overall, while there are risks associated with investing in bonds, the potential rewards can make it a worthwhile addition to your investment strategy. By being aware of the risks and taking steps to minimize them, you can help ensure that your bond investments are successful and profitable.